More than 700 varieties of jujube trees were identified in the improved objects, and it was difficult to distinguish breeds during the dormancy period or when the jujube was in the bud stage. It is necessary to determine the objects that need to be improved during the last fruit ripening period of the jujube fruit, and to determine quality varieties through visits and assessments, to avoid inadvertently improving the objects during the grafting period, blindly grafting, and sharing good and bad. If the whole park is grafted, this step is omitted.
Scion preparation First, determine the varieties and mother plants that need to be grafted. According to the above method, scion was collected on the better performing mother plant. Scion to collect the annual jujube tree is better, the scion must have bud eyes and full, no jujube disease and quarantine objects, the thickness of 0.4 to 0.8 cm, leaving 1 cm on the bud, leave 4 to 5 cm under the bud. After the scion was collected, the wax was sealed and the raw materials for sealing the scion were industrial paraffin. Wax sealing wax temperature should not be too high, to 70 °C ~ 80 °C is appropriate, too easy to scald buds, phloem and formation of scion layer, and not easy to store. After scion sealing, if it is not used immediately, it should be stored in cold storage and stored moist.
There are two kinds of grafting methods that are most suitable for the improvement of inferior varieties of jujube trees: grafting and cutting. Jujube peeling after skin grafting grafted than grafted survival rate is higher. There are three points to follow: to cut the surface to be flat, to form a layer to be aligned, and to be tight. The skin graft is also called the skin, this method is easy to learn, easy to operate, is a method of grafting survival rate is high, skilled grafted graft survival rate can reach 99%, but with the skin grafted improved varieties must wait until jujube After the skin can be carried out.
After grafting, there is a process of healing of the scion and rootstock forming layer. The dormant buds of the rootstock itself will germinate rapidly after being stimulated. This will result in the competition between the scion and the rootstock, and the buds must be timely and timely to make nutrients. Focus on the supply of scion to promote the healing of scion and rootstock. Generally, the bud is wiped every 3 to 5 days. Fertilizer management should generally be carried out before grafting, in order to promote the viability of rootstocks, to activate the formation of rootstocks, and to enhance the healing capacity of meristems in the formation layer, thereby increasing the survival rate.
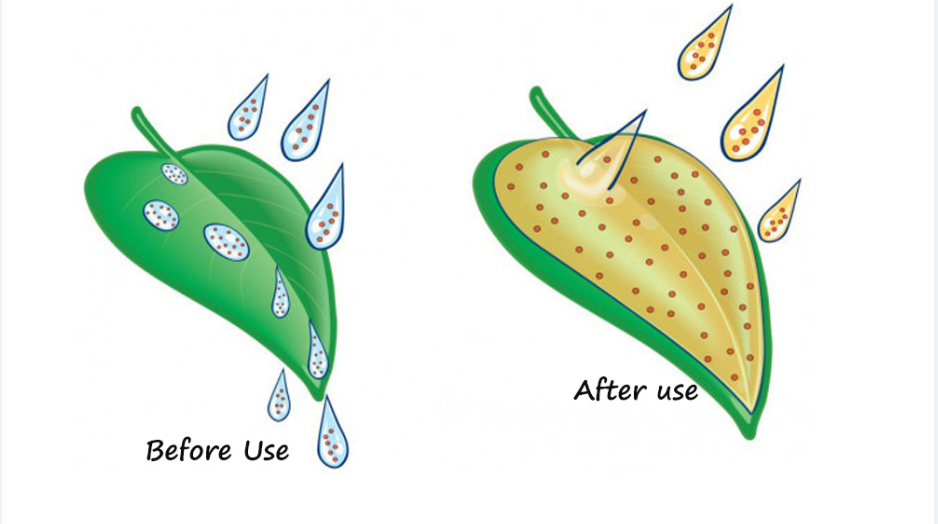
The Silicone Adjuvant is wetting and Penetrating Agent for the agrochemical.
Chemical name: Polyalkyleneoxide Modified Heptamethyltrisiloxane
Silicone adjuvant is a super-spreading surfactant based on a trisiloxane ethoxylate.
Spray Adjuvant lowers the surface tension of spray solutions, beyond that which is achievable with conventional adjuvants.
And,Silicone Surfactant promotes rapid uptake of agrochemicals into plants via stomatal infiltration.
spray adjuvant is nonionic in nature, making it useful with a broad range of agrochemical formulations.
Silicone Adjuvant
Silicone Additives,Silicone Adjuvant,Silicone Surfactant,Penetrating Agent,Polyalkyleneoxide Modified Heptamethyltrisiloxane
Jiangxi Tiansheng New Materials Co.,Ltd , https://www.jxtsxcl.com