The System Biomedical Collaborative Innovation Center led by Shanghai Jiaotong University, together with 17 hospitals from China's Blood/Tumor Clinical Multi-Center Research Institute (M-HOPES), has recently achieved important landmark results in lymphoma pathogenesis and clinical prognosis research. It fully embodies the purpose of multi-center multidisciplinary collaborative innovation and benefiting patients.
Natural killer T-cell lymphoma (NKTCL) is a special type of lymphoma with malignant proliferation of CD56+/cytoCD3+ lymphocytes. The disease is closely related to Epstein-Barr virus infection, which is relatively high in the Asian population, with serious risks and poor prognosis. However, because the pathogenesis of this disease has not been elucidated, it is a major challenge to find a disease-specific biomarker and treatment to effectively improve the efficacy of this type of lymphoma. The Shanghai Institute of Hematology from the System Biomedical Collaborative Innovation Center teamed up with 17 hospitals across the country to conduct genomics, molecular pathology, and clinical prognosis studies on NKTCL, a unique regional and clinically characterized blood tumor. Has achieved breakthrough results in the field of precision medicine.
Figure 1. NKTCL pathological section
The research team led by Academician Chen Saijuan, Academician Chen Wei and Professor Zhao Weilian of the System Biomedical Collaborative Innovation Center used the second-generation sequencing technology to sequence the whole exome of 25 NKTCL patients, and interpret the information of the gene coding region in the genome. The multi-center research facility platform was fully validated in an expanded sample of 80 patients with NKTCL.
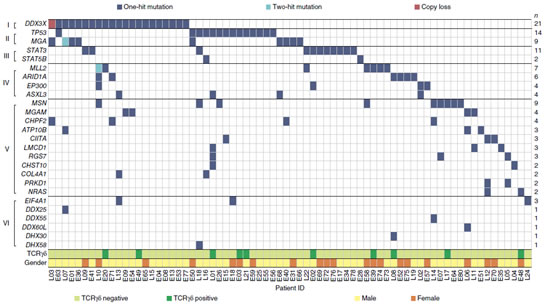
Figure 2. The team used mutations in whole-exome sequencing and target gene sequencing to screen for mutations in NKTCL cases.
The results showed that there is a high frequency mutation in the NKTCL, an important gene regulating RNA structure and function in the cell, and the mutation rate is the first in each gene mutation, and the mutation frequency of the tumor suppressor gene TP53 is second. The mutation rate of the two genes accounted for 32.4% of all gene mutations; while the DDX3X and TP53 gene mutations were mutually exclusive, suggesting that the pathogenesis of the two is highly correlated. Protein and cell function studies have shown that wild-type DDX3X protein has the effect of down-regulating nuclear RelB expression and reducing ERK phosphorylation, which inhibits cell proliferation and has the characteristics of tumor suppressor gene products, while DDX3X mutation leads to its encoded protein function. Inactivation leads to excessive cell proliferation.
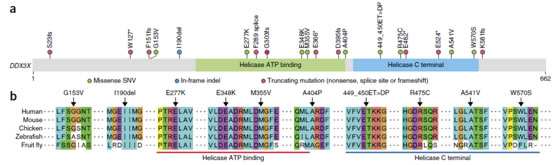
Figure 3 Mutations in the DDX3X gene in NKTCL cases (a) DDX3X gene mutation site map; (b) Sequence alignment of DDX3X protein in different species
The study also confirmed in a large group of cases that the DDX3X gene mutation is a molecular marker of poor prognosis in patients. At the same time, combined with TP53 mutation and the International Prognostic Index (IPI) of lymphoma, NKTCL patients can be further divided into three groups: Low-risk group (IPI index 0-1 and DDX3X and TP53 are wild type), medium-risk group (IPI index 0-1 and DDX3X and TP53 are mutant; IPI index 2-5 and DDX3X and TP53 are wild type) and high risk Group (IPI index 2-5 and DDX3X and TP53 are mutant). These results make the NKTCL clinical prognosis stratification more clear and rigorous, and provide potential targets for stratified precision treatment of the disease.
The results of this study were reported in the July 20, 2015 issue of Nature Genetics, which is by far the most comprehensive systematic genomics map of NKTCL, as well as the principle and clinical significance of the relevant mutation genes. The in-depth systematic explanation shows that Chinese scientists have become one of the world's most popular in the field of lymphoma research and have made important contributions to the development of lymphoma transformation medicine.
Technical review:
The development of second-generation sequencing and related technologies has greatly promoted the research of tumor genomics, which provides a solid theoretical basis for analyzing the mechanism of tumorigenesis and developing clinical diagnosis and treatment methods. Due to the strong heterogeneity of tumor tissue, there is a high depth requirement for sequencing. Exome sequencing and target gene sequencing can solve this problem. In this study, the team first used exome sequencing for small-scale screening (25 cases), and found a series of genes with higher mutation frequencies such as DDX3X and TP53, and then sequenced the target gene in a larger sample size. (80 cases) to verify mutations in these genes. This technical route is currently a relatively common practice, which not only saves the experimental cost, but also simplifies the data analysis process and ensures the sample size and sequencing depth.
In general, manual database construction of target gene sequencing is very cumbersome. The Access Array (Fluidigm) microfluidic platform used in this study greatly simplifies the construction of target genes. A 48.48 Access Array chip has 2304 PCR reaction chambers, and each reaction chamber can perform 1~10 PCR reactions. Using it, researchers can simultaneously amplify and build 48 to 480 target sequences for 48 samples. On this basis, in 2015, Fluidigm will soon launch the Orion-Juno multi-function micro-flow control database platform to meet the needs of researchers for different research projects. The 192.24 chip applied to this platform can simultaneously amplify and build up 1000~2500 target sequences of 192 samples, enabling researchers to complete more sample sequencing in one sequencing reaction, while a 48.48 chip can be used. A database of up to approximately 5,000 target sequences was completed for each sample to meet the researcher's high coverage research needs.
It is foreseeable that with the continuous advancement of related technologies, the experimental and labor costs of sequencing and building libraries in the future will be further reduced. This will have far-reaching implications for both basic and clinical research.
For more information on FLUIDIGM products, please contact us.
Fuluda (Shanghai) Instrument Technology Co., Ltd.
Http://cn.fluidigm.com
Phone mailbox:

                       (This report source: Xinhuanet / Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine, Ruijin Hospital, Institute of Hematology, website news)
Hydrocolloid Applicator 1.2*1.2
Hydrocolloid application contains a 100% hydrocolloid that covers the wound surface and medical Hydrocolloid Tape is used to absorb wound tissue fluid and maintain a moisture balance between the wound and the surrounding skin. Medical hydrocolloid dressing conforms to difficult body contours to protect superficial, minimally exudating wounds. Smooth outer surface helps protect skin from shear and friction.Conforms to even the most difficult body contours to provide a secure barrier for wound. Creates a moist environment to encourage wounds to heal.
Emergency hydrocolloid medical supply wound dressing are helpful for use on wounds that are:Clean and uninfected,Free of dirt or other debris,Dry with little to no drainage,Medium thickness.Because these dressings are flexible and water-resistant. Medical sterile adhesive Hydrocolloid Dressing for wounds also make an excellent protective layer for recently healed wounds, or for partly healed wounds with granulation tissue that needs protection from surface trauma. Furthermore, a emergency hydrocolloid medical supply blood wound dressing can mold around the wound and provide insulation so that the body doesn't need to use as much energy to heal the wound.
Generally, hydrocolloid surgical Dressing last from 3 to 7 days. Sometimes a hydrocolloid dressing Wet healing starts coming up at the edges earlier. If so, it needs to be changed earlier. Because they keep the wound moist and protected, the wound does not need to be cleaned daily. In fact, wounds covered by hydrocolloid wound dressing pads will heal faster if they are not regularly exposed to air.
Hydrocolloid Wound Dressing,Transparent Hydrocolloid Dressing,Hydrocolloid Gel,Thin Hydrocolloid Dressing
Henan Maidingkang Medical Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.mdkmedical.com