In the process of raising beef cattle, some farmers tend to increase the amount of concentrated feed in order to promote growth and improve meat quality. This often includes a large quantity of high-quality protein sources such as soybean meal, cottonseed meal, and peanut cake. While it is possible to add protein supplements to beef cattle diets, it's important to consider the specific needs of the animals at different stages of growth. Overfeeding protein can lead to digestive issues, waste of feed, increased costs, and even health problems, while underfeeding may result in poor growth and lower meat quality.
For steers weighing around 300 kg that are being fattened in a barn, the protein content in their diet should be between 10% and 13%. As they grow heavier, this percentage can gradually decrease. By the end of the fattening period, protein should make up about 10% of the total diet.
Calves under three months old have underdeveloped rumens and microbial populations, so their protein requirements are similar to those of monogastric animals. They need essential amino acids that they cannot produce on their own. Therefore, it's beneficial to include a variety of protein sources such as soybean meal and cottonseed meal in their feed. Combining these sources helps balance amino acid profiles. For example, soybean meal is rich in lysine and tryptophan but low in methionine, while cottonseed meal provides more methionine. Blending them improves overall nutrition. Adding feeds like wheat bran or alfalfa meal can also enhance protein intake. At this stage, protein should account for up to 20% of the diet.
For calves aged 6 to 12 months, with weights ranging from 150 to 200 kg, the protein content in their feed can be reduced to around 15%. As they continue to grow, this can be gradually lowered to 12%.
When fattening older cattle, the protein content in the diet should be kept at around 10%, but it’s crucial to include energy-rich feeds like corn, sorghum, and sweet potato chips to support overall development.
For high-grade beef cattle, the protein content in the diet should be increased by 2% to 3% compared to regular feeding practices to enhance marbling and meat quality. This adjustment ensures better results in premium beef production.
Melting point 500°C
Boiling point 64.6 °C
density 0.85 g/mL at 20 °C
Fp 52 °F
storage temp. Flammables area
solubility Soluble in methanol.
form powder
color White
Sensitive Moisture Sensitive
Lithium Methoxide CAS No.865-34-9
Lithium Methoxide Basic Information
CAS: 865-34-9
MF: CH3LiO
MW: 37.97
EINECS: 212-737-7
Mol File: 865-34-9.mol
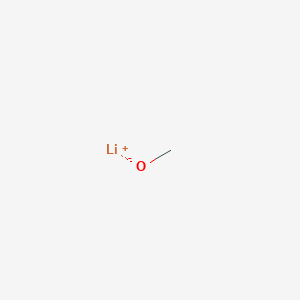
Lithium Methoxide Structure
Melting point 500°C
Boiling point 64.6 °C
density 0.85 g/mL at 20 °C
Fp 52 °F
storage temp. Flammables area
solubility Soluble in methanol.
form powder
color White
Sensitive Moisture Sensitive
Stability: Stable, but reacts violently with water. Highly flammable. Store under dry inert gas.
Lithium Methoxide Application
For organic synthesis reactions such as lipid exchange.
Lithium Methoxide,Lithium Methoxide Solution,Lithium Methoxide Formula,Lithium Methoxide Density,Lithium Methoxide Reaction
Shandong YingLang Chemical Co.,Ltd , https://www.sdylhgtrade.com